-

-
Imact of Bird Droppings on Flating Photovoltaic (FPV) Module Performance : Maintenance and Deterrence Methods
조류 배설물의 영향에 따른 수상태양광 시스템 성능 연구 : 유지보수 및 조류방지 방안
-
Myenggil Gang, Seong Dae Kim, Alex Lim, Choong sub Won, Hyunsik Jo, Jieun Lee, Chang-Sub Won
강명길, 김성대, 임민수, 원충섭, 조현식, 이지은, 원창섭
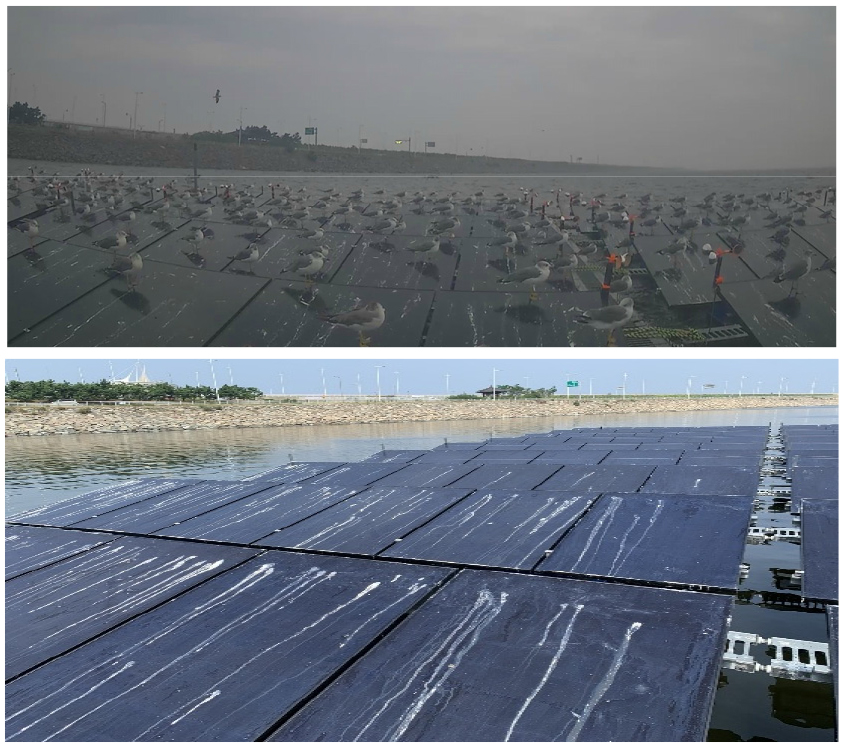
- This study examines the impact of bird droppings on the performance of floating photovoltaic (FPV) systems, with a focus on a case …
- This study examines the impact of bird droppings on the performance of floating photovoltaic (FPV) systems, with a focus on a case study conducted at the Marine Research Floating Photovoltaic (FPV) test-bed, installed in 2021 at Saemangeum, a seawater lake in South Korea. The FPV system was developed in collaboration with K-Water, a water resource management agency, for the purpose of establishing marine solar power facilities. During the research, environmental characteristics of the installation site led to the emergence of bird droppings as a significant issue, particularly due to the presence of seagulls and migratory birds, which pose a major challenge to the optimal operation of FPV systems. In bird-prone areas, these birds frequently utilize FPV sites as resting or sheltering locations. The deposition of bird droppings on FPV modules can severely affect energy efficiency, increase maintenance requirements, and compromise long-term system performance. The accumulation of droppings leads to shading, which reduces light absorption and consequently results in power output degradation. In some cases, this can also cause the formation of hotspots, which may accelerate the degradation of the modules. Moreover, the high uric acid content of bird droppings can damage the mechanical components of the photovoltaic system. This research investigates the effects of bird droppings on FPV module performance through on-site generation analysis. The study also explores various maintenance strategies and bird deterrence methods aimed at minimizing the impact of droppings and optimizing energy production. Practical solutions, such as robotic cleaning systems and bird-repelling technologies, are assessed for their effectiveness and feasibility in mitigating the adverse effects of bird activity. The findings of this study provide valuable insights into enhancing the sustainable operation of FPV systems, offering recommendations for improving maintenance efficiency and reducing performance losses associated with avian interference. - COLLAPSE
-
Imact of Bird Droppings on Flating Photovoltaic (FPV) Module Performance : Maintenance and Deterrence Methods
-

-
Analysis of Power Degradation and Status of Defect with Long Term Operation in Floating Photovoltaic
수상 태양광 장기 운영에 따른 불량 현황 및 출력 영향성 분석
-
Jieun Lee, Ji woo Sohn, Hyunsik Jo, Jungi Jeong, Won-wook Oh, Changsub Won, Donghwan Kim
이지은, 손지우, 조현식, 정준기, 오원욱, 원창섭, 김동환
- Photovoltaic (PV) technology is increasingly recognized as a key contributor to the global clean energy transition, highlighting the critical importance of long-term …
- Photovoltaic (PV) technology is increasingly recognized as a key contributor to the global clean energy transition, highlighting the critical importance of long-term module reliability. While Floating PV (FPV) systems are expected to exhibit degradation behaviors similar to ground-mounted systems, systematic field data on FPV module failures and performance impacts remain limited. In this study, FPV modules that had been in continuous operation for 13 years were analyzed to assess power degradation rates and failure modes, and to compare them with those of terrestrial PV systems. The results indicate that electrode corrosion accounted for 39% of observed defects. Notably, the average power degradation rate of FPV modules was 0.07%/yr, lower than typical values reported for land-based PV installations. This outcome suggests that although electrode corrosion increases series resistance, at the same time, it elevates parallel resistance, thereby contributing to enhanced durability under aquatic operating conditions. These findings provide novel insights into the long-term reliability of FPV systems and underscore the necessity of incorporating environment-specific degradation mechanisms into future module design and reliability assessment frameworks. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Power Degradation and Status of Defect with Long Term Operation in Floating Photovoltaic
-
-
Assessing the Economic and Market Implications of Solar PV Curtailment in Renewable Energy Projects and Power Purchase Agreements
재생에너지(태양광) 출력제어가 발전사업 경제성과 PPA 시장에 미치는 영향 분석
-
Hyun Gyu Lee, JongRoul Woo, Sung-Eun Chang
이현규, 우종률, 장성은
- This study quantitatively analyzes the impact of curtailment—a frequent phenomenon due to the expansion of renewable energy (solar PV)—on the profitability of …
- This study quantitatively analyzes the impact of curtailment—a frequent phenomenon due to the expansion of renewable energy (solar PV)—on the profitability of solar power projects and the Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) market. It evaluates how output reduction caused by curtailment affects key financial indicators such as the internal rate of return (IRR) and analyzes the changes in PPA pricing reflected by these losses. Using long-term industrial electricity tariff scenarios, the study assesses the price acceptance level of corporate PPA buyers, explores the structural gap between supply-side prices and demand-side willingness to pay, and examines the potential for market equilibrium. Policy and contractual adjustment mechanisms are evaluated using scenario-based analysis. By integrating curtailment, financial stability, PPA market trends, RE100-driven demand, and institutional compensation tools, this research provides practical insights for the sustainable development and regulatory design of Korea’s renewable energy-based direct power trading market. - COLLAPSE
-
Assessing the Economic and Market Implications of Solar PV Curtailment in Renewable Energy Projects and Power Purchase Agreements
-
-
Changes in Electrical Characteristics and Crop Yields of Agricultural Solar Systems Based on Module Installation Environment
모듈의 설치환경에 따른 영농형 태양광 시스템 전기적 특성 및 작물 생산량 변화
-
Seok Jin Jang, Jinjoo Park, Youngkuk Kim, Junsin Yi
장석진, 박진주, 김영국, 이준신
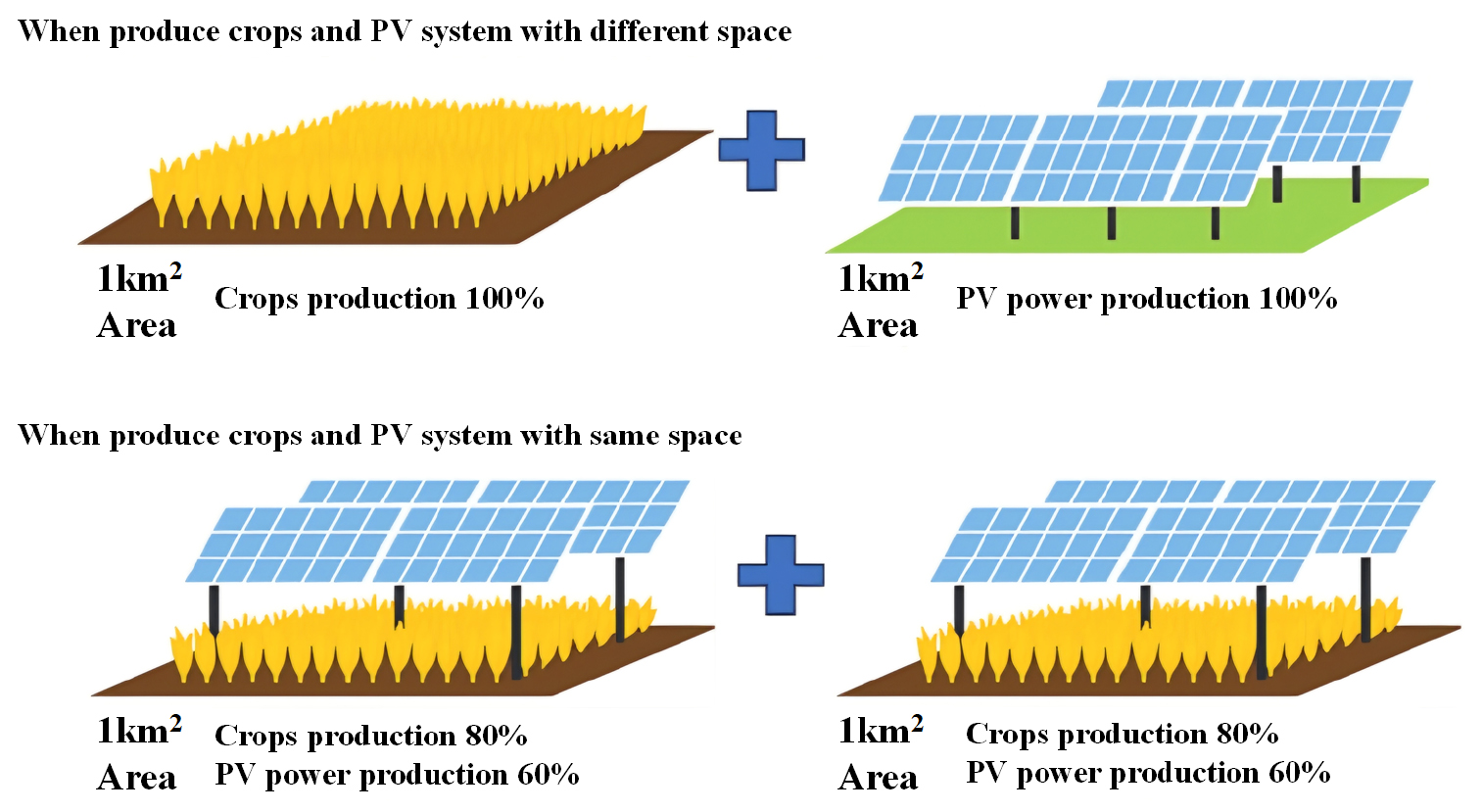
- Agricultural solar systems are highly space efficient systems that enable simultaneous agricultural and power production on the same farmland. The amount of …
- Agricultural solar systems are highly space efficient systems that enable simultaneous agricultural and power production on the same farmland. The amount of solar radiation reaching the ground surface and the degree of shading generated vary depending on the conditions of the installed modules, necessitating precise design. Using PVSYST simulation, we analyze the module’s power output, the solar radiation reaching the ground surface, and the PPFD and DLI while varying the module installation angle, azimuth angle, and the installation distance (pitch) between modules to predict the relative crop yield Results show that increasing tilt angle strongly improves ground PPFD/DLI by reducing ground shadow and enlarging sky and ground view factors. Higher tilted angle (60–90°) makes higher irradiance on the bottom ground and higher crop production. 30–45°. Wider pitch (≈6–10 m) further mitigates shading, lifting DLI to ≥20 mol/m2・day across the growing season. The recommended envelope for Korean agrivoltaics is high-tilt (≥60°) with ≥6 m pitch, balancing crop preservation and power output. - COLLAPSE
-
Changes in Electrical Characteristics and Crop Yields of Agricultural Solar Systems Based on Module Installation Environment
-
-
Research Trends of Aqueous Zinc-Iodine Batteries for Advanced Energy Storage Systems
차세대 에너지 저장 시스템을 위한 수계 아연 - 아이오딘 배터리의 연구 동향
-
Jihun Yoo, Yoongu Lim, Gyoung Hwa Jeong, Il Goo Kim, Kyung Wook Park, Young-Hoon Yun, Uk Sim
유지훈, 임윤구, 정경화, 김일구, 박경욱, 윤영훈, 심욱
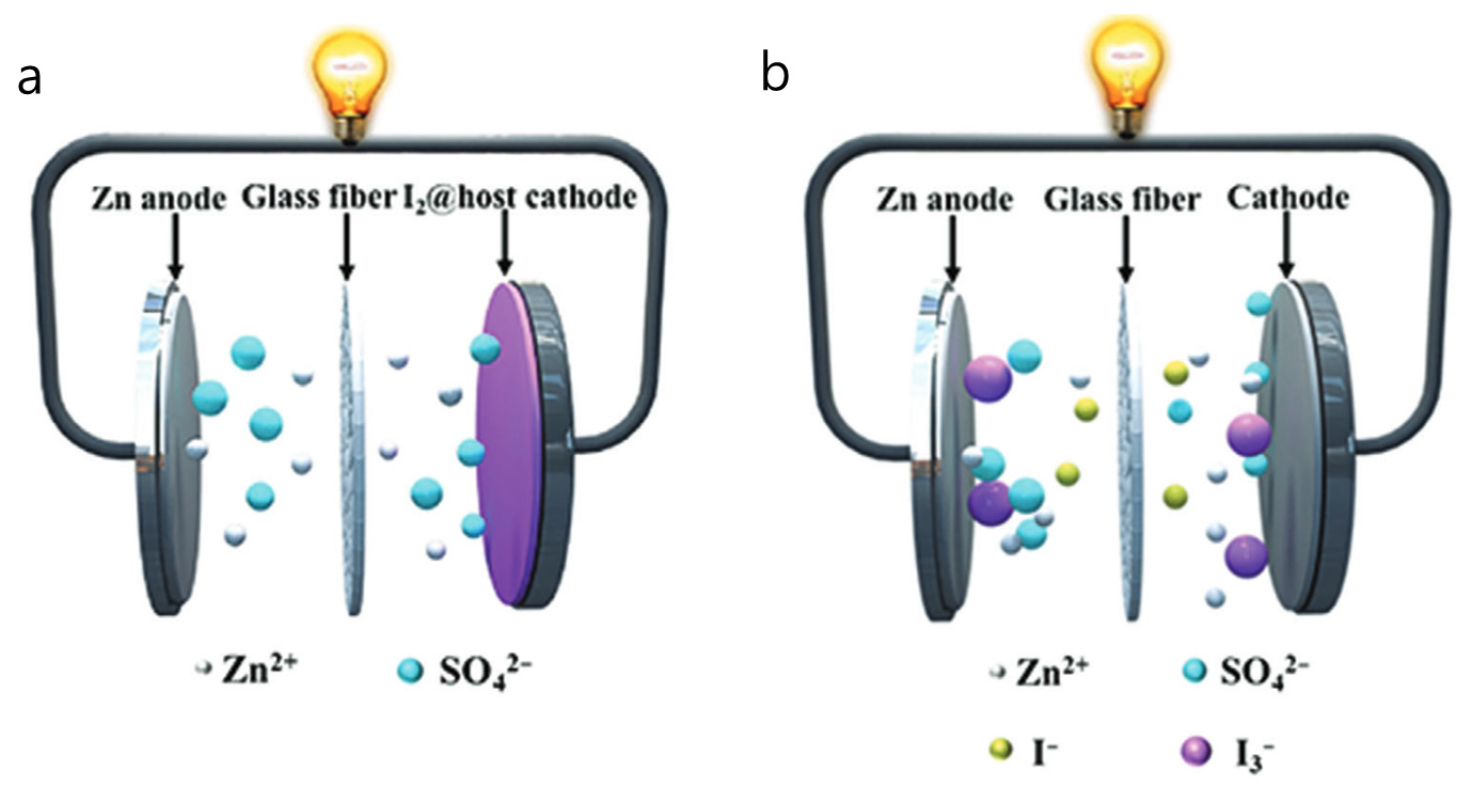
- The transition to sustainable energy systems requires next-generation rechargeable batteries that ensure high safety, energy density, and cost-effectiveness. Among emerging candidates, aqueous …
- The transition to sustainable energy systems requires next-generation rechargeable batteries that ensure high safety, energy density, and cost-effectiveness. Among emerging candidates, aqueous zinc–iodine (Zn–I2) batteries have gained attention owing to material abundance, intrinsic safety, and promising electrochemical performance. Iodine is abundant in seawater (55 µg L-1) and delivers a high theoretical capacity of 211 mAh g-1, while zinc offers a low redox potential and large storage capacity. Despite these merits, several inherent challenges limit practical application. The dissolution of polyiodide species and the resulting shuttle effect cause self-discharge and low Coulombic efficiency, while the zinc anode suffers from dendrite growth and side reactions such as hydrogen evolution. To address these issues, various strategies have been proposed, including cathode host design, electrolyte engineering, and anode stabilization. These approaches aim to suppress shuttle effects, regulate interfacial reactions, and promote uniform zinc deposition, thereby contributing to improved redox kinetics, higher Coulombic efficiency, and enhanced cycling stability. This review summarizes recent progress in Zn–I2 batteries and provides insights into rational design directions toward long-life, high-performance energy storage systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Trends of Aqueous Zinc-Iodine Batteries for Advanced Energy Storage Systems



 Current Photovoltaic Research
Current Photovoltaic Research







